ANATOMY OF LIVER
The Structure Of Liver
One of the largest internal organs in the human body, the liver weighs between 1.3 and 1.5 kg in an adult who is healthy. It carries out a wide range of tasks, such as preventing infections, clotting blood, producing different hormones and proteins, and more. Additionally, it is a gland, or more accurately, a glandular organ, because it secretes a variety of substances.
Located in the upper right corner of the abdomen, the liver is an organ (abdomen). The right kidney, stomach, and intestines are above it, and it is located below the diaphragm.
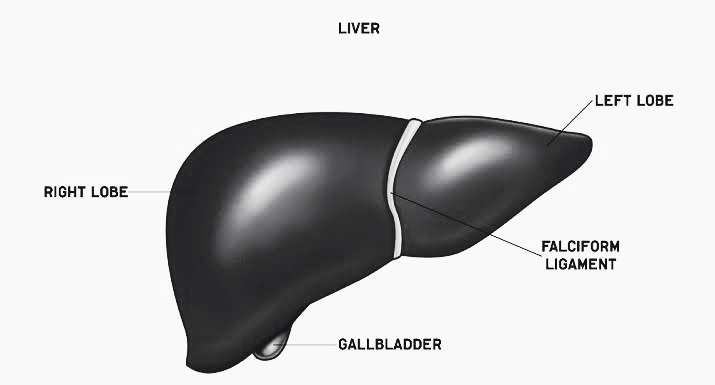
The liver is a triangular, bilobed organ with a larger right lobe and a smaller left lobe. The two lobes are divided by the falciform ligament.
The liver is covered with Glisson's capsule, a layer of fibrous tissue. The peritoneum surrounds this capsule. This shields the liver from harm physically.
Its two primary blood supplies are as follows:
Hepatic Portal Blood from the digestive tract is carried by veins because it is rich in nutrients.
Oxygenated blood is transported from the heart by the hepatic artery.
The liver contains two primary divisions (lobes). Each consist of 8 segments. One thousand tiny lobes make up each of the segments (lobules). The lobules are attached to tiny ducts (tubes), which eventually join with bigger ducts to form the common hepatic duct. Bile produced by the liver cells is transported through the common hepatic duct to the gallbladder and the first segment of the small intestine (the duodenum). A transparent yellow or orange fluid called bile aids in food digestion.
LIVER FUNCTIONS
Production of Bile
The liver produces bile, which aids in the digestion and absorption of fats, vitamins, and cholesterol.
1).ABSORPTION OF BILIRUBIN
The decomposition of haemoglobin produces bilirubin. In order to create new blood cells, the liver stores the iron that is released.
2).BLOOD CLOT SPOT
The absorption of vitamin K is mediated by bile. Bile production is a prerequisite for the production of clotting factors.
3).Mineral and vitamin storage
The liver stores vitamins A, D, E, K, and B12. Ferritin, a kind of iron storage, is also used to create new red blood cells.
4).Fat Metabolization
The breakdown and digestion of lipids are aided by bile.
5).Metabolization of Carbohydrates
To keep blood sugar levels stable, the carbohydrates stored as glycogen in the liver are converted to glucose and released into the blood.
6).Protein Metabolic Process
Protein digestion is aided by bile.
7).Blood Filtration
The liver filters substances from the blood, including hormones, alcohol, and other substances.
8).Immunological Activity
Kuffer cells that are engaged in immunological function are found in the liver. They eliminate any potential pathogens.
9).Producing Albumin
Fatty acids and steroids are transported by albumin to maintain proper pressure and stop blood vessel leakage.
10).Synthesis of Angiotensinogen
It is this hormone that causes blood vessels to constrict, raising blood pressure as a result.
11).Liver regeneration
All vertebrates have the capacity for liver regrowth. The liver maintains its functions throughout the growing period. Regeneration takes 8 to 15 days in humans.
The similar procedure takes about 5-7 days in mice.
12).produces bile, which aids in digestion by assisting with the removal of waste and the breakdown of fats in the small intestine.
13).produces certain proteins for blood plasma
14).produces specific proteins and cholesterol to aid in the movement of fats through the body.
Thank you ☺️
Best of luck
Zeeshanfayazlone@



Comments
Post a Comment